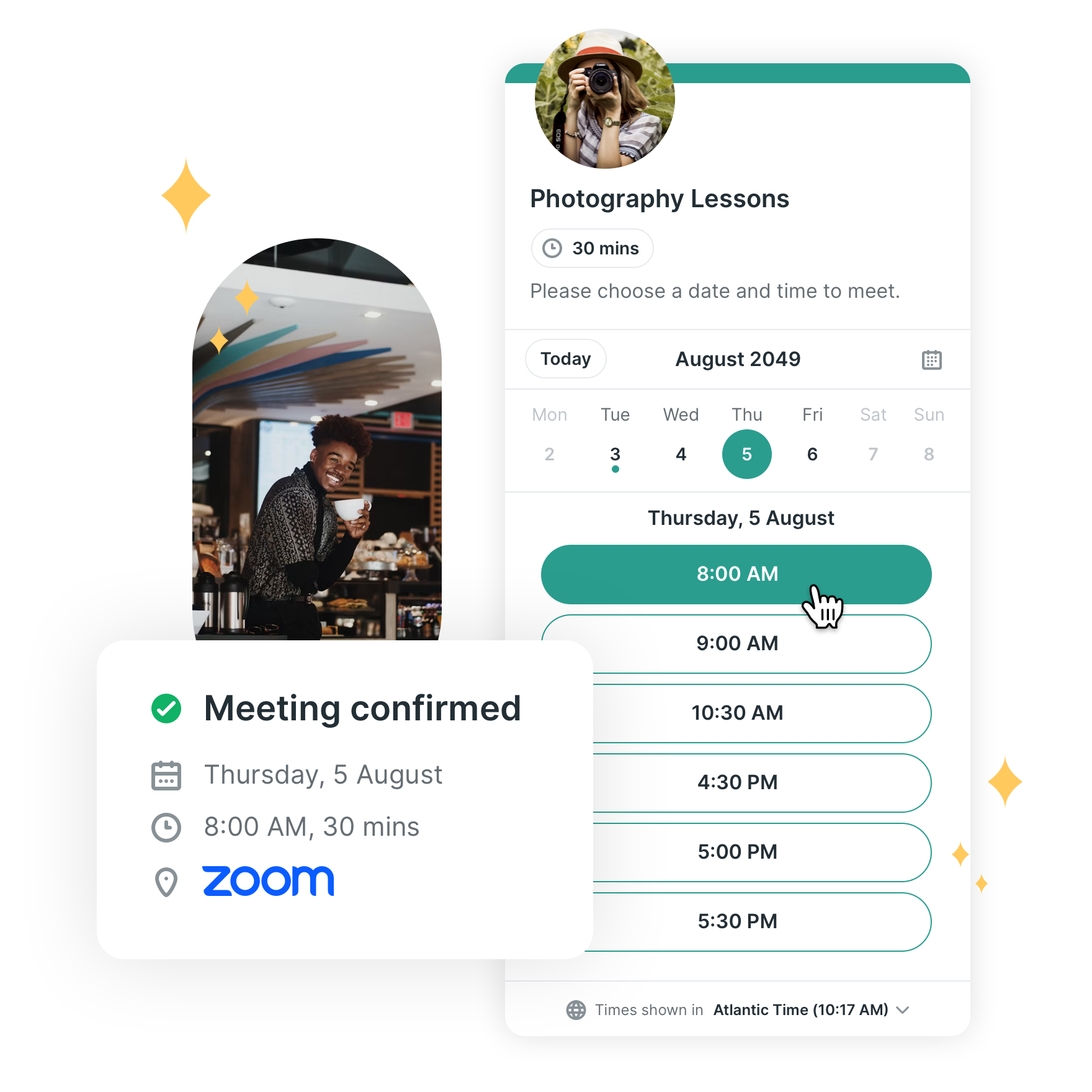
What Is Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools?
Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools act as the operational bridge between a business's available resources—whether human capital, physical assets, or time slots—and the external demand for those resources. At its core, this software category digitizes the negotiation of time. It replaces the friction of asynchronous communication (email tag, phone tag) with a deterministic, real-time booking engine that enforces business logic regarding availability, qualification, and routing.
This category covers software used to manage the allocation of time-based inventory across the customer lifecycle: facilitating initial prospect meetings, coordinating service delivery appointments, managing recurring client check-ins, and optimizing internal resource utilization. It sits between CRM (which manages the relationship data) and ERP (which manages the financial and operational backend), specifically governing the "when" and "who" of service execution. It includes both general-purpose scheduling platforms suitable for horizontal use (e.g., sales demos, consulting calls) and vertical-specific tools built for complex operational environments like healthcare patient intake, field service dispatching, and logistics dock management.
Who uses these tools? While early adopters were primarily in personal services (salons, solo practitioners), usage has scaled to the enterprise enterprise. Sales development teams use them to increase speed-to-lead; healthcare networks use them to reduce patient leakage and no-show rates; logistics coordinators use them to prevent detention fees at warehouses. It matters because the "booking" is often the first point of commitment in a commercial relationship. Friction here results in revenue loss, while efficiency here drives asset utilization and customer lifetime value.
History of Appointment Scheduling
The evolution of appointment scheduling software is a case study in the shift from static record-keeping to dynamic, autonomous logic. In the 1990s, "scheduling" was largely a digitized version of the paper ledger. Early solutions were on-premise desktop applications, often isolated within a local area network. They served as a database of record—a place to type in a name after a phone call was completed. The primary value proposition was legibility and storage, not efficiency or automation. Integration with other systems was virtually non-existent, creating data silos where the "schedule" had no visibility into the "customer record" stored in early Contact Management systems.
The late 1990s and early 2000s saw the emergence of the first web-based scheduling tools, coinciding with the broader dot-com boom. Companies like TimeTrade (now Engageware) pioneered the concept of self-service scheduling [1]. This was a paradigm shift: moving the administrative burden from the staff to the customer. However, adoption was initially slow due to consumer hesitation regarding internet security and the nascent state of real-time calendar synchronization. During this period, the gap between CRM and scheduling became painfully obvious. Sales teams using early versions of Salesforce (launched in 1999) still had to manually reconcile their booked meetings with their pipeline data.
The rise of the API economy and the explosion of SaaS in the 2010s fueled the next major wave. General-purpose tools like Calendly and Acuity Scheduling commoditized the "booking link," making individual productivity tools accessible to the masses. Simultaneously, vertical SaaS began to dominate complex industries. Field service management, healthcare, and beauty industries demanded tools that didn't just book a time but also handled the specific metadata of that industry—HIPAA compliance for doctors or route optimization for plumbers. By the mid-2010s, the market had bifurcated into these simple productivity tools and heavy, vertical-specific platforms.
Today, we are in the era of "Intelligent Scheduling." The expectation has shifted from "give me a database" to "give me actionable intelligence." Modern platforms are expected to use AI to predict no-shows, optimize route density dynamically, and automate complex round-robin assignments based on real-time revenue data. Market consolidation has accelerated, with major CRM and ERP players acquiring standalone scheduling engines to close the loop between "intent" and "action." As detailed in G2's 2025 Buyer Behavior Report, buyers now prioritize AI-driven efficiency and operational integration over simple feature lists, marking a maturity in the category where software is judged by its ability to autonomously manage time rather than just record it [2].
What to Look For
Evaluating appointment scheduling software requires looking past the glossy "booking page" to the backend logic that governs your operations. The most critical evaluation criterion is calendar logic flexibility. A robust tool must handle complex availability scenarios—such as buffer times, travel time calculations (for field services), and resource pooling (where multiple staff members share one room or piece of equipment). Ask vendors specifically about "concurrency rules": Can the system prevent a user from being double-booked across different service types, or does it merely look at free/busy status?
A major red flag is a system that relies solely on one-way calendar syncs. Enterprise-grade scheduling requires two-way synchronization with practically instant latency. If a sales rep blocks off time for a dentist appointment in their Outlook calendar, the scheduling tool must reflect that unavailability within seconds to prevent a prospect from booking that slot. Delays of even a few minutes can lead to double bookings, which damage brand reputation. Furthermore, look for "orphan record" management. When an employee leaves, does their booked calendar data vanish, or can it be easily reassigned to a new owner? Inadequate data governance during offboarding is a frequent point of failure.
Key questions to ask vendors include:
- "How does your system handle time zone conversions for recurring appointments across daylight savings time shifts?" (This breaks many basic tools).
- "Can we implement round-robin routing that prioritizes high-performing reps or specific territories before falling back to general availability?"
- "What is the API rate limit for checking availability, and does your webhooks system support 'event rescheduled' triggers distinct from 'event cancelled' and 'event created'?"
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Retail & E-commerce
In retail, appointment scheduling has evolved from a VIP perk to a core operational necessity. The primary use case here is omnichannel continuity. Retailers use these tools to bridge the digital-physical divide, allowing customers to book in-store consultations, personal shopper sessions, or "buy online, pick up in-store" (BOPIS) slots. The critical evaluation priority is the mobile experience; the booking interface must be embedded seamlessly into the retailer’s consumer app or loyalty portal without requiring a separate login. Retailers also require robust queue management features that can handle walk-ins alongside pre-booked appointments, dynamically adjusting wait times.
Unique considerations for retail include "resource-dependent" bookings. For example, a bridal shop cannot simply book a stylist; they must simultaneously reserve a fitting room. Software that cannot link these two resources (human and spatial) will lead to logistical failures on the sales floor. Furthermore, integration with Point of Sale (POS) systems is non-negotiable. The scheduling tool should pass customer preference data (collected during booking) to the associate's tablet, enabling a personalized greeting and higher conversion rates.
Healthcare
Healthcare scheduling is governed by triage logic and regulatory compliance. Unlike a business meeting, a medical appointment often requires a pre-qualification sequence to determine urgency and appropriate provider level. Tools in this space must support complex decision trees—"If symptoms X and Y are present, block 30 minutes with a specialist; otherwise, block 15 minutes with a nurse practitioner." Security is paramount; any tool selected must be HIPAA-compliant (in the US) or GDPR-compliant (in Europe), with Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) readily available. The cost of failure is high; 2024 saw a record number of healthcare data breaches, exposing over 276 million patient records, often due to third-party vendor vulnerabilities [3].
Reducing no-show rates is the primary ROI driver. Healthcare providers should look for tools with multi-channel automated reminders (SMS, Email, Voice) that require active confirmation. Advanced systems now use predictive analytics to identify patients at high risk of no-showing and automatically overbook those specific slots or send additional reminders. The ability to integrate with Electronic Health Records (EHR) via standards like HL7 or FHIR is essential to ensure that the appointment data flows directly into the patient's medical history.
Financial Services
For wealth management and banking, the focus is on trust and relationship continuity. High-net-worth clients expect a frictionless, white-glove experience. Scheduling tools here must look and feel like a proprietary part of the firm's brand, not a third-party add-on. The ability to route a client specifically to their assigned advisor—rather than a generic pool—is critical. "Sticky routing" ensures that if a client clicks a generic "Book a Meeting" link, the system recognizes their email and offers slots only from their dedicated relationship manager.
Compliance features regarding record retention are unique to this sector. FINRA and SEC regulations often require that all communications regarding trade instructions or financial advice be archived. Therefore, the scheduling tool's notification emails and SMS logs must be ingestible by the firm's archiving solution. Additionally, integration with wealth management CRMs (like Salesforce Financial Services Cloud) allows advisors to see a client's total assets under management (AUM) alongside their booking history, enabling more prepared and productive meetings [4].
Manufacturing
Manufacturing and logistics utilize "Dock Scheduling" software, which is functionally distinct from human appointment booking. The "client" here is a truck, and the "service provider" is a loading bay. The critical pain point is detention time—the fees manufacturers pay when carriers wait too long to load or unload. These tools must integrate with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS) to validate purchase orders (POs) before a slot is even offered. If a carrier tries to book a delivery for a PO that isn't in the system, the software must block the attempt.
Evaluation priorities focus on constraint management. Can the system handle constraints like "Freezer Dock" vs. "Dry Dock," or "Palletized" vs. "Floor Loaded" cargo? A standard calendar cannot distinguish these variables. The software must also support "standing appointments" for regular carriers while dynamically opening up spot-market slots. Real-time visibility is crucial; according to industry reports, inefficient dock scheduling is a primary driver of supply chain bottlenecks, leading to ballooning operational costs [5].
Professional Services
Consultancies, law firms, and agencies require billable utilization tracking. Scheduling in this context is often tied to project codes and billable hours. The software needs to differentiate between a "non-billable business development call" and a "billable client consultation." Integration with time-tracking and invoicing software is the key differentiator. If a client books a one-hour consultation, the system should be able to automatically generate a draft invoice or deduct credits from a retainer.
Unique considerations include "complex panel scheduling." Professional services often involve panel interviews or multi-stakeholder meetings (e.g., a client review with a Partner, a Manager, and an Associate). The tool must be able to find the intersection of availability across three internal calendars and the external client, a computational problem that simple booking links often fail to solve effectively. Resource allocation reports are also vital, helping firm leaders understand which consultants are overbooked and which have capacity [6].
Subcategory Overview
Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for Plumbers
This niche is fundamentally about route density and dispatch efficiency. Generic scheduling tools optimize for calendar availability, but plumbing software optimizes for geography. If a technician has a job in North London at 9:00 AM, a generic tool might allow a 10:00 AM booking in South London, creating an impossible travel itinerary. Specialized plumbing tools integrate map data to present availability based on travel time buffers between jobs. They handle "emergency override" logic, where a burst pipe call can dynamically reshuffle lower-priority maintenance jobs.
One workflow that ONLY this specialized tool handles well is the "on-my-way" notification sequence. These platforms automate a specific chain of communication: a booking confirmation, a reminder 24 hours prior, and crucially, a GPS-triggered SMS when the technician is en route, often including a photo of the technician for homeowner safety. This specific pain point—homeowners not knowing when to expect the tradesperson—drives buyers away from generic calendars toward tools like Housecall Pro or ServiceTitan. For a deeper look into these features, see our guide to Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for Plumbers.
Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for Contractors
Contractor scheduling differs because it deals with project dependencies rather than isolated time slots. A general contractor cannot schedule the drywall installation until the electrical and plumbing inspections are marked complete. Generic tools treat appointments as independent events; contractor-specific software treats them as sequential dependencies in a Gantt chart. If the framing is delayed by two days, the software must automatically shift the tentative bookings for the electricians and painters forward, notifying all subcontractors instantly.
The specific pain point driving buyers here is subcontractor coordination. Managing a shifting timeline across five different external companies using Google Calendar is impossible. Specialized tools allow "tentative" booking requests that are confirmed only when the preceding task is finished. They also often include file uploads for permits and blueprints directly within the appointment record, ensuring the crew has the necessary documentation upon arrival. Learn more about managing these complex timelines in our guide to Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for Contractors.
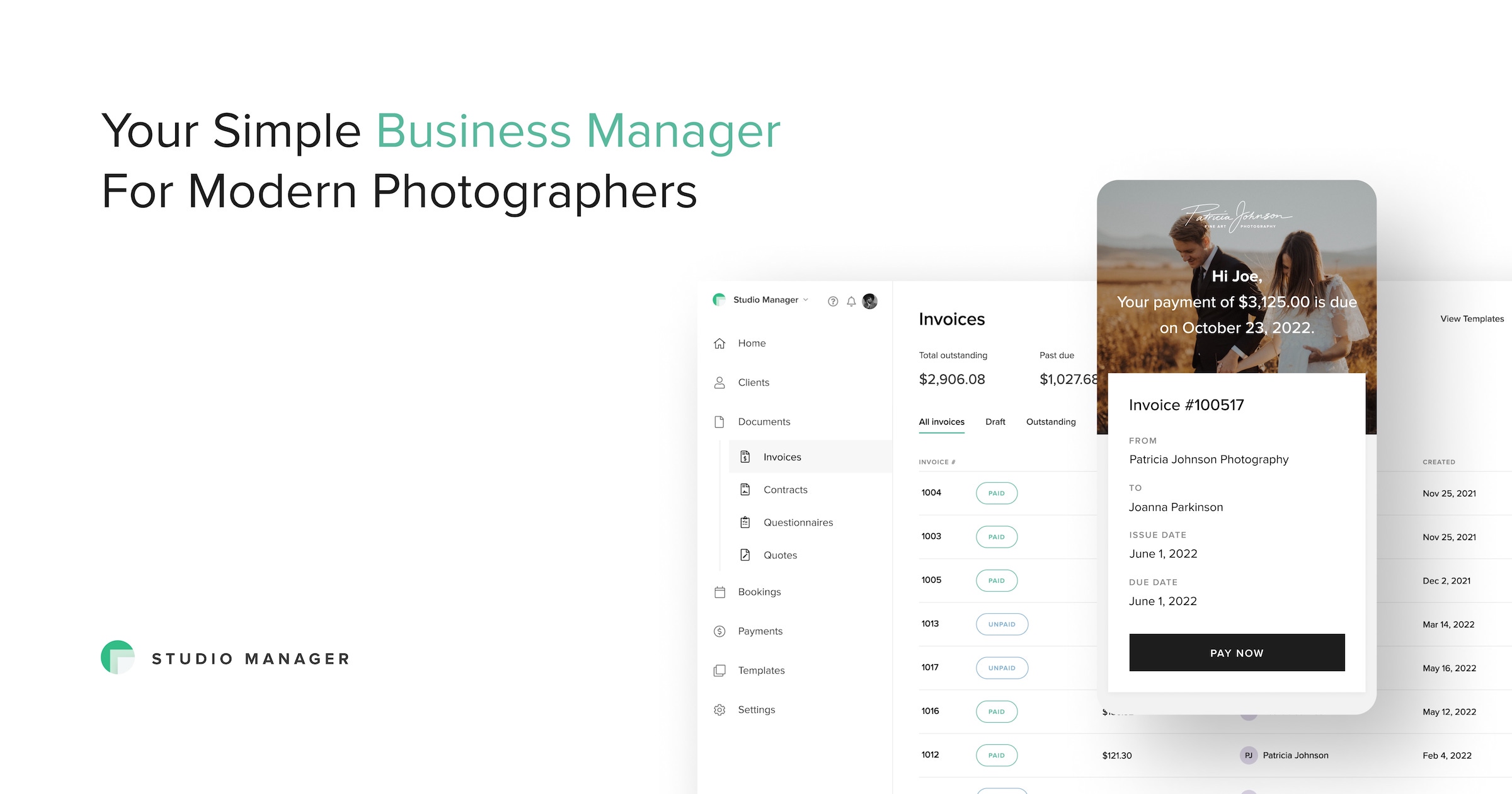
Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for Photography Studios
For photographers, the booking process is inextricably linked to workflow automation and asset delivery. A generic tool books the time, but photography-specific software manages the lifecycle: booking, contract signing, retainer payment, shoot execution, and gallery delivery. The unique workflow here is the "Mini-Session" booking event—a high-volume, back-to-back scheduling frenzy where a photographer might book 20 clients in one day. These tools offer specialized "session slot" interfaces that allow clients to grab 15-minute increments from a pre-defined block, handling the rapid-fire payments and automated confirmation emails that would crash a manual system.
The driving pain point is client image selection and upselling. Buyers choose niche tools (like HoneyBook or specialized gallery plugins) because they integrate the booking with the proofing gallery. After the shoot, the system automatically triggers an email to book the "viewing session," linking directly to the revenue-generating phase of the service. Generic tools create a disconnect between the service delivery and the product delivery. Explore these visual-centric features in our guide to Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for Photography Studios.
Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for SaaS Companies
SaaS companies use scheduling tools as a revenue acceleration engine. The primary differentiator here is Lead-to-Account matching and advanced Round-Robin logic. Unlike a salon where the client chooses the provider, in SaaS, the business chooses the rep. Specialized tools analyze the prospect's email domain or form data (e.g., company size: Enterprise), match it against the Salesforce territory map, and display availability only for the appropriate Account Executives. If the assigned AE is busy, it might route to a secondary pool, but the logic is strictly governed by revenue rules.
The workflow that only these tools handle is the handoff from SDR to AE. An SDR (Sales Development Rep) cold calls a prospect and needs to book a demo for an AE immediately. SaaS-specific scheduling tools provide a "book on behalf of" interface that credits the meeting to the SDR (for commission) while placing it on the AE's calendar. The pain point driving this choice is "speed to lead"—generic tools introduce friction or misrouting that lowers conversion rates on high-value inbound traffic. Read about optimizing these funnels in our guide to Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for SaaS Companies.
Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for Private Equity Firms
In Private Equity (PE), scheduling is a function of deal flow management and relationship intelligence. The stakes are incredibly high; a missed meeting with a founder or intermediary can mean losing a deal. Unlike high-volume SaaS scheduling, PE tools focus on "white-glove" coordination and long-term nurturing. These platforms often integrate with relationship intelligence data (like Affinity or specialized CRMs) to surface context before the meeting: "Who in our firm last spoke to this founder?" "What is the status of their latest funding round?"
The unique workflow is the multi-party deal coordination involving internal investment committees, external legal counsel, and the target company's management. Specialized tools offer "suggested times" functionality that polls internal availability for high-priority partners without exposing their full calendars to external parties. The pain point driving buyers to this niche is data privacy and the need to track "interaction velocity"—using meeting frequency as a proxy for deal heat. Discover how top firms manage their pipeline in our guide to Appointment Scheduling & Booking Tools for Private Equity Firms.
Integration & API Ecosystem
In the modern tech stack, a scheduling tool that stands alone is a liability. The value of these tools is realized when they act as the trigger for broader business processes. A named statistic from Gartner highlights that poor data integration costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually, a figure that underscores the financial risk of disconnected systems [7]. Integration must go beyond simple calendar syncing. It requires robust APIs that can handle webhooks, custom objects, and bi-directional data flow.
Forrester analysts have noted that "API-first" architecture is becoming a primary selection criterion, as legacy systems often hit rate limits that throttle high-volume booking environments. A concrete example of this plays out in mid-sized professional services firms. Imagine a 50-person consultancy that connects its scheduling tool to Salesforce (CRM) and QuickBooks (Invoicing). In a poorly designed integration, when a client reschedules a consultation from January to February, the scheduling tool updates the calendar but fails to update the "Service Delivery Date" in the CRM. Consequently, the invoicing system triggers a bill for January, confusing the client and creating an accounting reconciliation nightmare. A robust integration would use webhooks to listen for the "Reschedule" event and automatically cascade that date change across the CRM and billing platforms, ensuring data integrity.
Security & Compliance
Security in appointment scheduling is no longer just about password protection; it is about data sovereignty and regulatory adherence. With the rise of cyber threats, the scheduling interface is a vulnerable entry point that collects Personally Identifiable Information (PII) before a user is even authenticated. According to a 2024 report by Sprinto and HIPAA Journal, the healthcare sector alone saw data breaches exposing over 276 million records, driven largely by third-party vendor vulnerabilities [3]. Buyers must demand SOC 2 Type II compliance, and for specific industries, HIPAA or GDPR compliance is non-negotiable.
Gartner's VP of Research emphasizes that "security assessments must extend to the vendor's sub-processors," meaning you must know who hosts your scheduling provider's data. Consider a scenario in a Private Equity firm dealing with sensitive M&A targets. If their scheduling tool creates "public" booking links that are indexed by search engines, a savvy competitor could potentially scrape these links to identify who the firm is meeting with, effectively leaking the deal pipeline. Secure tools allow for "expiring links," password-protected booking pages, and domain-restricted access (e.g., only allowing bookings from email addresses matching specific domains), preventing this type of corporate espionage.
Pricing Models & TCO
Pricing in this category is deceptive. The "per-user" license fee is often just the tip of the iceberg. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) calculations must include add-ons for SMS credits, payment processing fees (often 2.9% + 30¢ per transaction), and premium integration connectors (e.g., connecting to Salesforce often bumps you to an "Enterprise" tier). Recent data suggests that companies are wasting significant budget on unused software; Zylo’s 2024 SaaS Management Index reveals that organizations use only 47% of their provisioned SaaS licenses, essentially throwing away nearly half of their spend [8].
Let's walk through a TCO calculation for a 25-person sales team. A "Pro" plan might be advertised at $15/user/month ($4,500/year). However, if the team sends 50 automated SMS reminders per day, and the vendor charges $0.04 per SMS, that adds another $500/month ($6,000/year)—more than the software license itself. Add in a mandatory $2,000 "onboarding fee" for the Salesforce integration and a 20% premium for "SSO (Single Sign-On)" security features. The perceived cost of $4,500 quickly balloons to over $15,000 annually. Buyers must model these usage-based variables (SMS, payments, API calls) to avoid budget shock.
Implementation & Change Management
The software is easy to buy but hard to enforce. The failure rate for digital transformation projects remains high; McKinsey reports that nearly 70% of digital transformations fail to meet their original goals, largely due to employee resistance and lack of management support [9]. In the context of scheduling, "shadow IT" is the enemy. If half the team uses the new enterprise tool and the other half clings to their personal Calendly links or manual emails, the data reporting becomes useless.
A real-world failure scenario involves a manufacturing firm implementing a new Dock Scheduling System. The headquarters purchases a sophisticated platform to optimize loading bay times. However, the gate guards and warehouse foremen—who actually manage the trucks—find the mobile interface too small for their rugged tablets. They revert to using a physical whiteboard to track arrivals. The result? The software shows the docks are empty, while in reality, trucks are backed up down the street. Successful implementation requires "user acceptance testing" (UAT) with the actual end-users in their physical environment, not just the IT team in the office.
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
When selecting a vendor, buyers must look beyond feature matrices to the vendor's market durability and support ecosystem. Forrester's research into B2B buying behavior indicates that buyers are increasingly dissatisfied with post-sale support and the "expertise" demonstrated by vendors, leading to stalled implementations [10]. A critical criterion is the vendor's "ecosystem density"—how many pre-built integrations do they have? A vendor with 500+ native integrations is a safer long-term bet than one requiring custom API work for every connection.
Consider a rapidly scaling SaaS company evaluating vendors. They choose a startup scheduling tool because it has a "modern UI." Six months later, the company acquires a competitor and needs to merge two Salesforce instances. The scheduling vendor lacks the enterprise support to handle multi-tenant CRM connections. The SaaS company is forced to rip and replace the tool during a critical merger integration, costing hundreds of hours in lost productivity. Buyers should ask for "Reference Architectures" during the evaluation phase—proof that the vendor has successfully supported clients with similar tech stack complexities.
Emerging Trends and Contrarian Take
Emerging Trends (2025-2026): The most significant shift is the move toward Agentic AI. We are moving past "automated scheduling" to "autonomous negotiation." By 2026, AI agents will not just offer slots but will actively negotiate times, reschedule conflicts, and prioritize meetings based on strategic value without human intervention. Gartner predicts that by 2026, 40% of enterprise applications will include embedded AI agents to automate these complex workflows [11]. Additionally, we will see a convergence of "Scheduling" and "Project Management," where the booking of a meeting automatically generates the associated task dependencies in tools like Asana or Monday.com.
Contrarian Take: The standalone calendar interface is dying.
The industry is obsessed with building better "booking pages," but the smartest buyers realize that the best booking experience is no booking page. The future isn't a better link you send via email; it is "invisible scheduling" embedded directly into the workflow—where a voice assistant listens to a call and books the follow-up automatically, or a chatbot on a website books the demo without ever opening a calendar view. Businesses investing heavily in "destination" scheduling portals are fighting the last war; the mid-market is overpaying for UI when they should be investing in API-led headless scheduling infrastructure.
Common Mistakes
The most pervasive mistake buyers make is overbuying for "theoretical" complexity. Organizations often purchase "Enterprise" tiers for features like "resource pooling" or "territory management" that they think they need, only to realize their actual workflow is linear. This leads to "bloatware" where the user interface is so cluttered with unused features that adoption drops. Conversely, underestimating change management is fatal. Leaders assume that because the tool is "easy to use," no training is required. They fail to mandate the retirement of old methods (e.g., "stop using email for internal meetings"), creating a fractured ecosystem where availability data is never accurate because half the meetings aren't in the system.
Another critical error is ignoring the "reschedule" workflow. Buyers test the "happy path" (booking a meeting) but rarely test the "unhappy path" (canceling and rescheduling). If the rescheduling process is high-friction, customers will simply no-show. A robust system must make rescheduling as one-click simple as the initial booking.
Questions to Ask in a Demo
- Concurrency: "If I have three different booking types (15min, 30min, 60min), how does your system optimize the calendar to prevent 'swiss-cheese' gaps where 15 minutes are stranded between hour-long calls?"
- Data Retention: "What happens to the data of a user who is deleted? Does their historical appointment data persist for reporting, or is it wiped?"
- Latency: "What is the specific sync latency between your platform and Outlook/Google? Is it real-time push, or a polling interval (e.g., every 5 minutes)? 5 minutes is too long for our high-volume sales team."
- Localization: "Does the frontend interface automatically detect and translate to the user's browser language, or is it a manual toggle?"
- API Governance: "Do you offer a sandbox environment for us to test integrations before pushing to production?"
Before Signing the Contract
Final Decision Checklist:
- Security Audit: Has your InfoSec team reviewed their SOC 2 report and penetration testing results?
- Integration Validation: Have you successfully connected the tool to your sandbox CRM and verified bi-directional data flow?
- User Role Verification: Does the system support "granular permissions" (e.g., a junior rep can view but not edit a manager's calendar)?
- Support SLA: Does the contract guarantee response times for "System Down" events? "Email support" is often insufficient for mission-critical operations.
Deal-Breakers: Avoid vendors who lock you into long-term contracts without a "pilot period" opt-out. Be wary of "proprietary" calendar systems that do not sync natively with Google/Microsoft; these create islands of data that are impossible to maintain. Finally, ensure there are no hidden "overage" fees for high volumes of bookings or API calls.
Closing
Selecting the right appointment scheduling tool is not just an administrative decision; it is a strategic choice about how your organization values time—both yours and your customers'. If you have specific questions about matching a tool to your unique workflow or need clarification on a vendor's capabilities, please reach out.
Email: albert@whatarethebest.com