
The following research highlights a significant shift in Requirements Management (RM): the transition from manual, document-based tracking to AI-driven, automated traceability. Recent market data reveals that automated traceability coverage surged from 54% in 2022 to 72% in 2024, driven by the integration of AI tools that act as collaborative partners rather than replacements for human eng
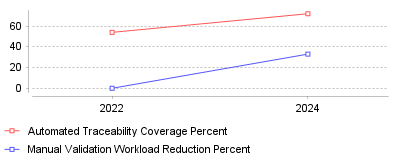
| Year | Automated Traceability Coverage Percent | Manual Validation Workload Reduction Percent |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 54 | 0 |
| 2024 | 72 | 33 |
Data from recent market reports indicates a massive leap in the adoption of automated tooling within the Requirements Management sector. Specifically, automated traceability coverage increased from 54% in 2022 to 72% in 2024 [1]. Concurrently, a survey of software practitioners reveals that 58.2% of professionals are now actively using AI in Requirements Engineering (RE), with the vast majority favoring a "Human-AI Collaboration" (HAIC) model over full automation [2]. This data proves the industry is moving away from static requirements matrices toward dynamic, data-centric systems.
On a micro level, this trend signifies the death of the "spreadsheet traceability matrix." The 18-point jump in automated coverage has directly resulted in a 33% reduction in manual validation workloads, allowing engineers to focus on architecture rather than administrative compliance [1]. On a macro industry level, this represents a stabilization of AI utility; the market has rejected "AI as a replacement" (only 5.4% of teams use full AI automation) in favor of "AI as a Co-pilot," where AI handles the tedious linking of artifacts while humans retain decision-making authority [3]. Additionally, this shift supports a "data-centric" view where documents are merely snapshots of live data, enabling real-time synchronization of over 1,200 requirement artifacts per project cycle [1].
As software complexity grows, manual requirements management has become a primary failure point for large-scale projects. The improved traceability is critical for regulated industries (Automotive, MedTech, Aerospace), where 64% of enterprises now mandate strict traceability across at least six project phases [1]. Furthermore, AI tools are proving superior at quality control; AI-enabled analysis is now detecting ambiguity in 45% of requirement statements, effectively reducing defect leakage by 27% before development even begins [1].
The sudden acceleration in 2023-2024 is likely fueled by the commoditization of Large Language Models (LLMs) which excel at processing the natural language found in requirement documents—a task previous generations of tools struggled with. The sharp rise in "Human-AI Collaboration" specifically suggests that while confidence in AI's *processing* power has grown, trust in its *autonomy* remains low, leading teams to adopt tools that verify rather than create [2]. Additionally, the increasing cost of compliance and the complexity of "connected" products (IoT) have likely forced organizations to abandon manual methods that can no longer scale [4].
The requirements management landscape has fundamentally changed: it is no longer about documenting needs, but computing connections between them. The substantial increase in automated traceability (reaching 72%) combined with high AI adoption rates confirms that AI is becoming the standard infrastructure for handling project complexity. The key takeaway for leaders is that Human-AI Collaboration (HAIC) has emerged as the winning operating model, delivering efficiency without sacrificing the human oversight required for safety-critical decision making.
Software quality failures cost the U.S. economy $2.41 trillion in 2022 [1]. This figure, calculated by the Consortium for Information & Software Quality (CISQ), accounts for operational failures, unsuccessful projects, and the accumulation of technical debt. Requirements errors—defects introduced during the definition phase—remain the most expensive to correct. IBM Systems Sciences Institute data reveals that fixing a defect during the maintenance phase costs 100 times more than fixing it during the requirements phase [2]. As engineering teams face tighter compliance mandates, the sector for requirements management and spec tools has shifted from passive document storage to active risk mitigation.
The market for these tools is expanding to meet this pressure. Analysts project the global requirements management software market will reach approximately $4.76 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.8% [3]. This growth is not merely a function of IT spending; it reflects a survival mechanism for regulated industries. Medical device manufacturers and automotive OEMs now face penalties that threaten their balance sheets. Philips Respironics, for instance, agreed to a $1.1 billion settlement in 2024 to resolve personal injury litigation related to its CPAP recall, a crisis stemming from material specification and change management failures [4].
Vendors are aggressively integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) into their platforms to automate requirements authoring and traceability. PTC launched Codebeamer 3.2 with "Codebeamer AI" in early 2026, offering features to generate test cases directly from requirements [5]. Similarly, Visure Solutions added AI capabilities to automate the generation of functional requirements and compliance checklists [6].
This automation introduces a critical operational risk: accuracy. A systematic literature review analyzing 238 papers on Generative AI in requirements engineering found a hallucination rate of 63.4% [7]. In this context, hallucination refers to AI generating requirements that sound plausible but conflict with source inputs or contain fictional constraints. For safety-critical sectors, this error rate is unacceptable. While product spec tools with design and engineering collaboration features can speed up drafting, the human burden shifts from authorship to verification.
The operational challenge lies in "interpretability." The same study noted that 57.1% of research identified the opacity of LLM decision-making as a barrier to trust. Engineers cannot easily trace why an AI model suggested a specific tolerance or safety margin. Consequently, organizations adopting these tools must implement rigid "human-in-the-loop" validation processes, negating some of the promised efficiency gains. The current trend suggests AI will serve as a drafting assistant rather than an autonomous engineer for the foreseeable future.
The FDA intensified its enforcement activities in 2024, creating immediate demand for stricter traceability tools. The agency issued 47 warning letters to medical device manufacturers in fiscal year 2024, a 96% increase from the 24 letters issued in 2023 [8]. This surge signals a departure from the FDA's previous "integrative approach," moving instead toward rapid enforcement when inspection findings are not adequately addressed.
Specific violations drove this increase. Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) failures appeared in over 60% of enforcement actions [8]. Manufacturers failed to link complaints to root causes and design changes. This disconnect highlights the operational failure of legacy systems where risk analysis, requirements, and testing live in separate silos. Enterprise buyers are responding by consolidating these functions. They are replacing disparate spreadsheets with requirements management tools for enterprise products that enforce a digital thread from the initial user need to the final validation record.
Data integrity also emerged as a primary focus. Inspectors flagged missing raw data and audit trail gaps in 2024-2025 inspections [9]. 21 CFR Part 11 compliance—governing electronic records—is no longer a checkbox; it is a trigger for warning letters if audit trails are not immutable and complete. Tools that allow "soft deletes" or unrecorded modifications of requirements are becoming liabilities.
Automotive manufacturers face a similar regulatory cliff. UNECE Regulation 155 (R155) became mandatory for all new vehicles produced from July 2024 [10]. This regulation requires OEMs to implement a Cybersecurity Management System (CSMS) that spans the entire vehicle lifecycle. It is no longer sufficient to secure a car at the point of sale; manufacturers must manage risks through post-production software updates.
ISO/SAE 21434 serves as the engineering standard to meet these R155 requirements. It mandates that cybersecurity requirements be treated with the same rigor as functional safety requirements (ISO 26262). The operational impact is severe: every line of code and every electronic control unit (ECU) requirement must trace back to a Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA) [11].
Suppliers are struggling with this data exchange. An OEM might use IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management (ELM) while a Tier 1 supplier uses PTC Codebeamer or Jama Connect. Exchanging complex specification data between these systems often relies on the Requirements Interchange Format (ReqIF). However, "round-trip" data loss remains a persistent operational headache. When attributes defined in one tool do not map cleanly to another, critical safety parameters can disappear. To combat this, platforms like IBM ELM 7.1 have introduced "digital thread" improvements to manage dependencies across heterogeneous tools using OSLC (Open Services for Lifecycle Collaboration) linking rather than simple file exports [12].
While specialized engineering tools handle the "V-model" of development, they often disconnect from the broader project management ecosystem. This separation creates a visibility gap. The Project Management Institute (PMI) reported that organizations prioritizing "power skills" (communication, strategic thinking) alongside technical skills see 72% of their projects meet business goals, compared to a lower rate for those that do not [13]. However, even skilled teams fail when their tools isolate them.
The separation of requirements from task management leads to scope creep. PMI data indicates that 28% of projects experience scope creep even in high-performing organizations [13]. When a requirement changes in a spec tool but the corresponding task in Jira or Asana does not update, developers continue working on obsolete specs. To bridge this gap, teams are increasingly adopting requirements tools integrated with issue tracking. This integration ensures that a status change in a requirement automatically flags the associated engineering tasks, preventing wasted effort.
Siemens addressed this in its Polarion X 2506 release by adding "Scheduled Scripts" to automate workflow steps across connected systems, attempting to force synchronization where manual updates often fail [14]. The goal is to make project management and productivity tools act as a unified nervous system rather than disjointed limbs.
The requirements management sector is moving toward a convergence of safety, security, and sustainability. The separation between "functional requirements" (what the product does) and "non-functional requirements" (security, safety, compliance) is disappearing. In 2025 and beyond, a requirement for a braking system will inherently include its cybersecurity attributes (ISO 21434) and its functional safety level (ISO 26262) in a single data object.
Governance will become the primary differentiator for tool selection. As AI agents begin to generate code and test cases, the "requirement" becomes the only human-readable constraint in the loop. If the requirement is vague, the AI will generate valid code that produces the wrong product. The role of the requirements engineer will evolve into that of a "prompt auditor," using tools that mathematically verify the logic of a spec before it ever reaches a developer or an AI agent.