Introduction Research into the financial performance of major collaboration platforms reveals a striking divergence in growth trajectories between multi-product "Work OS" platforms and traditional project management tools. Specifically, while competitors like Asana and monday.com operated with comparable revenue figures in 2021 and 2022, a significant gap emerged in 2023 that has widened aggressively through 2024 and 2025. This trend highlights a market shift where growth is increasingly driven by multi-product suites (e.g., dedicated CRM and Development products) rather than generic task
| Year | monday.com Revenue ($M) | Asana Revenue ($M) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 308 | 378 |
| 2022 | 519 | 547 |
| 2023 | 730 | 653 |
| 2024 | 972 | 724 |
| 2025 (TTM) | 1166 | 774 |
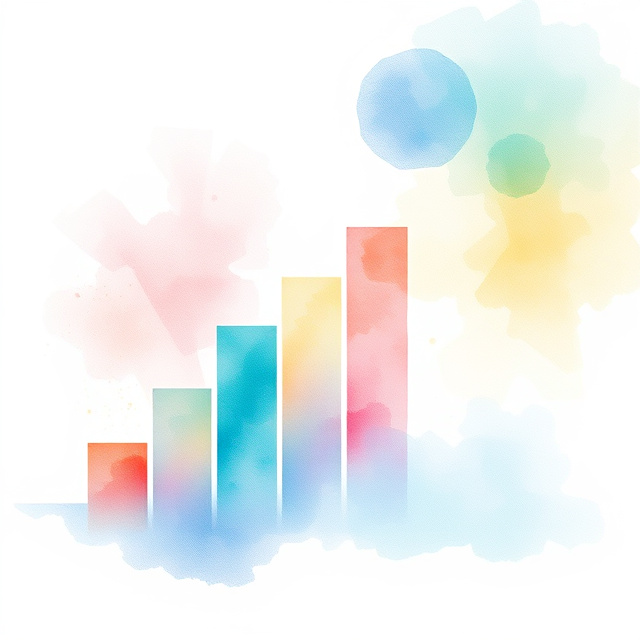
The data illustrates a dramatic "revenue crossover" and subsequent divergence between two market leaders, monday.com and Asana, occurring over the last 36 months. While Asana led in revenue generation during 2021 and maintained parity through 2022, monday.com accelerated significantly in 2023, overtaking Asana and establishing a massive lead by 2025 [1]. As of the most recent trailing twelve-month (TTM) data from late 2025, monday.com's revenue has surged to approximately $1.17 billion, reflecting a ~30% year-over-year growth rate, whereas Asana's growth has slowed to approximately 9-10%, reaching only $774 million [2][3].
This trend signifies a fundamental shift in the collaboration software industry from single-category tools to comprehensive "Work Operating Systems" (Work OS). The market is heavily rewarding vendors that have successfully pivoted from being just "project management" tools to becoming multi-product platforms that serve distinct business functions like CRM, software development, and service management [4]. For the broader industry, it suggests that the era of generic horizontal collaboration tools is ending; enterprises now prefer consolidated stacks where one vendor provides specialized solutions for different departments (Sales, Dev, HR) on a unified data backbone. This divergence indicates that companies failing to diversify their product lines risk stagnation, while multi-product platforms capture the majority of new enterprise spend [1].
This is critical because it redefines the competitive baseline for SaaS companies in the productivity space; high growth is now dependent on "land and expand" strategies that cross departmental lines. The data shows that monday.com's ability to cross-sell specific products (like monday CRM and monday Dev) allowed it to maintain high net retention and growth rates even during a macro-economic slowdown, while competitors with a singular focus faced fiercer headwinds [4][5]. Furthermore, the sheer scale of the revenue gap (widening to over $390 million in TTM differences) suggests a "winner-takes-most" dynamic is solidifying in the enterprise work management category.
The primary driver appears to be the strategic launch of product-specific suites—specifically monday CRM and monday Dev—which allowed the company to capture budget from non-project management buckets (like sales software), effectively expanding their Total Addressable Market (TAM) [6]. Conversely, Asana focused heavily on refining its core project graph and enterprise "C-suite" visibility features but was slower to launch distinct, standalone product lines for non-project use cases [1]. Additionally, aggressive innovation in AI-backed automation and "Digital Workers" may have accelerated adoption for platforms viewed as more adaptable to replacing manual administrative work [7].
The data confirms that the collaboration market has bifurcated: multi-product platforms are accelerating while pure-play project management tools are plateauing. For buyers, this suggests that "Work OS" platforms offer better long-term viability and consolidation potential. The prominent takeaway is that in 2025, sustainable growth in this sector demands a multi-product architecture that can monetize specific departmental workflows, not just general collaboration.

The landscape of modern work is undergoing a profound structural shift, driven by the rapid maturation of Collaboration & Work Management Platforms. As organizations transition from the reactive digital adoption of the early 2020s to a more strategic consolidation phase, the market for collaboration software has swelled, with valuations estimated between $14.16 billion and $18.2 billion in 2024, projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 7.7% to 13.5% over the coming decade [1], [2], [3].
However, this growth masks significant operational friction. While digital tools were intended to streamline productivity, an over-saturation of disparate applications has created a "toggle tax" that drains employee focus and efficiency. Simultaneously, the integration of artificial intelligence—specifically "Agentic AI"—is redefining how work is executed, yet adoption gaps between management and frontline workers threaten to create a two-tiered workforce. This report analyzes the critical trends, operational challenges, and vertical-specific implications defining the current state of Project Management & Productivity Tools.
The most pressing operational challenge facing enterprises today is the fragmentation of the digital workspace. In the rush to support remote and hybrid environments, organizations have accumulated an unmanageable stack of point solutions.
Research indicates that the average knowledge worker now utilizes approximately 11 distinct applications to complete daily tasks, a significant increase from just six in 2019 [4], [5]. This fragmentation forces employees to constantly switch contexts, a phenomenon known as the "toggle tax."
The operational impact of this fragmentation is measurable and severe:
Business leaders are increasingly recognizing that simply adding more tools does not equate to higher productivity. Instead, the market is trending toward platform consolidation, where disparate functionalities (messaging, task management, file storage) are unified into a single "system of work" to reduce cognitive load [8].
Artificial Intelligence is shifting from a passive assistive feature to an active agent in work management. However, the deployment of these technologies has revealed a stark disparity in adoption rates across organizational hierarchies.
While 78% of managers and leaders report using AI tools regularly (several times a week), only about 51% to 52% of frontline employees do the same [9], [10]. This gap, termed the "Silicon Ceiling," suggests that while leadership envisions an AI-enabled future, the necessary tools, training, and permissions are not effectively cascading down to the operational level.
The implications of this divide are two-fold:
The next frontier in work management is "Agentic AI." Unlike passive chatbots that wait for prompts, AI agents are designed to autonomously plan, execute, and complete multi-step workflows [12], [13]. By 2025, these agents are expected to handle complex tasks—such as processing payments, checking for fraud, and coordinating logistics—without human intervention [13].
For operational leaders, the challenge shifts from merely adopting AI to governing a workforce where digital agents interact with human employees. This requires a fundamental redesign of workflows to accommodate non-human actors, a transition that many legacy data architectures are currently ill-equipped to support [14].
While the "toggle tax" and AI integration are universal challenges, the operational impact varies significantly across industries. Specialized sectors are increasingly rejecting generic tools in favor of vertical-specific platforms that address their unique workflows.
The construction industry faces a unique "field-to-office" disconnect. Operational efficiency relies heavily on the real-time flow of information between on-site crews and project managers. Generic tools often fail to handle the complexity of BIM (Building Information Modeling) data, RFI (Request for Information) tracking, and safety compliance in a mobile-first environment.
Leading Collaboration & Work Management Platforms for Contractors are evolving to bridge this gap by integrating mobile field reporting with back-office ERPs. Key trends include:
For plumbing businesses, the operational challenge is often logistical: efficient dispatching, inventory management, and maximizing billable hours. The digital transformation in this sector is driven by the need to reduce administrative overhead and improve response times.
Modern Collaboration & Work Management Platforms for Plumbers are focusing on:
Roofing contractors face distinct challenges related to estimation accuracy and safety. Manual measurements are dangerous and time-consuming, while generic project management tools lack the specificity required for aerial estimation.
Emerging Collaboration & Work Management Platforms for Roofing Companies are leveraging advanced imaging technology to solve these problems:
In the high-stakes world of Private Equity (PE), operational challenges center on "deal flow" and "relationship intelligence." Generic CRMs often fail to capture the nuanced, multi-stakeholder relationships that drive investment decisions.
Specialized Collaboration & Work Management Platforms for Private Equity Firms are addressing this by moving beyond simple contact management:
As collaboration tools become the central nervous system of the enterprise, they also become a primary attack vector. The reliance on these platforms has exposed organizations to significant vulnerabilities.
With 79% of workers utilizing digital collaboration tools, the potential for security incidents has skyrocketed [27]. The casual nature of chat platforms (Slack, Teams) often leads employees to let their guard down, resulting in a higher click rate on phishing links compared to traditional email [28].
Furthermore, the "Shadow AI" problem mentioned earlier poses a severe data governance risk. When employees feed sensitive corporate data (customer lists, proprietary code, internal strategy) into unapproved public AI models to increase productivity, that data effectively leaves the secure corporate perimeter [11].
Business Implication: Organizations must move beyond simple access controls and implement "Zero Trust" architectures within collaboration platforms. This includes granular data governance policies that specifically address AI usage and the automatic detection of sensitive data sharing within chat and project management streams.
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, the collaboration market will be defined by the convergence of automation and work management.
1. The Rise of Hyperautomation:
We are moving toward an era of "hyperautomation," where AI agents and integration platforms (iPaaS) connect disparate tools to automate end-to-end business processes [12]. The goal is to reduce the "toggle tax" not just by consolidating apps, but by having the software perform the switching and data transfer autonomously.
2. Work Management as a System of Record:
Collaboration platforms are evolving from simple communication hubs into the primary "system of record" for work [29]. Just as Salesforce is the system of record for customer data, platforms like Asana, Monday.com, and industry-specific tools are becoming the definitive source of truth for operational activity, status, and performance metrics.
3. Conclusion:
For decision-makers, the path forward involves a rigorous audit of the current tech stack. Reducing the number of overlapping tools, investing in vertical-specific solutions where generic ones fail, and establishing clear governance for AI adoption are the critical steps to navigating the next phase of collaborative work.