Global OKR Software Market Revenue Projections (Billions USD)
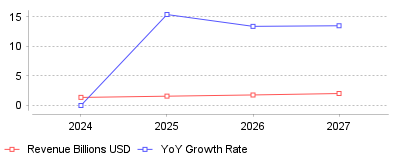
| Year | Revenue Billions USD | YoY Growth Rate |
|---|
| 2024 | 1.36 | N/A |
| 2025 | 1.57 | 15.4% |
| 2026 | 1.78 | 13.4% |
| 2027 | 2.02 | 13.5% |
The Shift from Reporting to Prediction: AI-Enabled Decision Intelligence
What is this showing
The data reveals a rapid acceleration in the valuation of the OKR software market, driven primarily by the integration of Artificial Intelligence features. Specifically, the market is projected to grow from $1.36 billion in 2024 to $1.78 billion in 2026, representing a compound annual growth rate exceeding 13% [1] [2]. More importantly, this financial growth correlates with a functional shift: approximately 55% of organizations are now adopting AI-enabled goal tracking solutions, and 45% of new productivity software releases in 2024 included AI-based features like predictive task management [3] [4].
What this means
For the software industry, this signals the end of "static" goal tracking where users manually input progress percentages. The new standard is "Decision Intelligence," where software uses Neural-Level Precision to analyze internal data (like CRM or Jira logs) to auto-update goals and predict performance drops before they occur [5]. At a macro level, this transforms OKR platforms from administrative reporting tools into strategic "central nervous systems" for enterprises [5]. For micro-users (employees), it means the commoditization of strategy drafting; AI agents now assist with drafting OKRs, performing quality checks, and providing smart alignment recommendations, significantly lowering the barrier to entry for complex strategy frameworks [6].
Why is this important
This trend is critical because it addresses the historic failure rate of strategic execution; roughly 69% of enterprises using traditional management tools report goal misalignment within three months of execution [5]. By automating the connection between daily tasks and high-level objectives, companies using modern OKR software are reporting 50% higher employee engagement rates and 30% faster decision-making cycles [2]. Furthermore, the dominance of cloud-based deployment (78% market share) ensures these AI insights are available to distributed workforces, which is essential for maintaining alignment in hybrid work models [2].
What might have caused this
The primary catalyst is the ubiquity of Generative AI (LLMs), which solved the "blank page problem" that previously made writing good OKRs difficult for non-executives [7]. Additionally, the permanent shift to remote and hybrid work (where remote work accounted for nearly 40% of the global workforce by 2024) necessitated digital tools that could autonomously "nudge" employees toward alignment without constant manager intervention [4]. Finally, the economic pressure to optimize efficiency has driven companies to seek tools that reduce "human lag"—the time between a market shift and a change in company strategy—effectively forcing software vendors to build adaptive, real-time systems [5].
Conclusion
The OKR software market is no longer just about tracking goals; it is about automating the intelligence required to achieve them. As we move toward 2026, the data suggests that platforms lacking AI-driven predictive capabilities and automated integration will likely become obsolete. The prominent takeaway for buyers is that the value of these tools now lies in their ability to reduce decision latency, turning strategy execution into a real-time, data-responsive process rather than a quarterly administrative burden.
The Shift from Output to Outcome: State of the OKR Software Market
The global landscape for goal management is undergoing a structural transition, shifting from simple task tracking to complex strategy execution. As organizations grapple with distributed workforces and economic volatility, the demand for Objectives and Key Results (OKR) software has surged, yet operational friction remains a critical barrier to value realization. The market for
OKR & Goal Tracking Software is projected to grow from approximately $1.57 billion in 2025 to over $5.5 billion by 2035, driven by a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) exceeding 13%
[1].
However, this growth masks a turbulent operational reality. While adoption is rising, successful implementation is far from guaranteed. Research indicates that nearly 70% of OKR implementations fail to achieve their intended strategic outcomes, often due to a disconnect between high-level strategy and daily execution
[2]. The market is currently characterized by a dichotomy: the pressing need for alignment tools versus the fatigue of "double entry"—where employees must update goal progress in a dedicated platform separate from where their actual work occurs.
This report analyzes the current trends, operational bottlenecks, and future outlook for the goal tracking software industry, with specific focus on the implications of AI integration and major market disruptions like the retirement of Microsoft Viva Goals.
Market Disruption: The Sunset of Microsoft Viva Goals
A defining event for the 2025-2026 operational landscape is Microsoft's decision to retire Viva Goals. Formerly Ally.io, a market leader acquired by Microsoft in 2021, Viva Goals will officially be discontinued on December 31, 2025, with all feature development halted as of late 2024
[3].
This development has profound implications for enterprise IT and operations leaders:
- Forced Migration: Thousands of organizations embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem must now migrate data and retrain staff on alternative platforms. Microsoft has explicitly stated there will be no direct internal replacement, forcing users to evaluate third-party vendors [4].
- Market Redistribution: Competitors such as Quantive, WorkBoard, and Profit.co are aggressively positioning themselves to capture this displaced user base, emphasizing "seamless migration" paths and feature parity [5].
- Integration Skepticism: The retirement validates concerns regarding the longevity of non-core modules within broader productivity suites. It forces buyers to reconsider whether goal tracking should live within a generalist suite or a dedicated "best-of-breed" platform.
For organizations currently navigating this transition, the focus has shifted from "adoption" to "continuity," ensuring that historical performance data is not lost during the migration to new
Project Management & Productivity Tools.
Operational Challenge: The "Double Entry" Friction
The single most significant operational complaint regarding OKR software is the "swivel chair" effect. This occurs when employees manage tasks in execution platforms (like Jira, Asana, or Salesforce) but are required to manually update progress in a separate OKR tool.
The Data Silo Problem
When goal tracking is decoupled from work execution, data integrity suffers. Users often update OKRs only right before a meeting, leading to "status reporting" rather than "performance management." This manual friction is a primary driver of the high failure rates in OKR adoption.
Modern solutions are attempting to solve this through deep integration. For example, platforms that can automatically update a Key Result (e.g., "Launch 3 features") when a specific Epic is closed in Jira eliminate the need for manual reporting [6]. However, achieving this level of automation requires rigorous data governance and standardization of how work is tracked—a maturity level many organizations lack.
Workflow-Native Goals
The trend is moving toward "workflow-native" goals. Instead of logging into a separate portal, employees update goals directly within communication tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams. This reduces the barrier to entry and keeps goals visible. For software-focused organizations, selecting specialized
Goal & OKR Management Tools for SaaS Companies that integrate natively with engineering stacks is becoming a prerequisite for reducing operational friction.
Trend Analysis: AI and "Agentic" Execution
Artificial Intelligence is shifting OKR software from passive repositories to active coaching systems. In 2024 and 2025, the focus has moved beyond simple generative text (e.g., "Write an OKR for Sales") to predictive execution.
Predictive Analytics
Leading platforms now use historical data to forecast the probability of goal achievement. By analyzing past cycle times and current progress rates, AI can flag "at-risk" objectives weeks before a human manager might notice a slip
[7]. This shifts management from reactive damage control to proactive resource allocation.
Agentic AI
The emerging frontier is "Agentic AI"—systems capable of executing multi-step workflows to help achieve goals. Rather than just tracking a metric, an AI agent might analyze a lagging Key Result (e.g., "Increase web traffic") and autonomously propose a list of SEO optimizations or draft a marketing campaign for review
[8]. This represents a fundamental change in the software's role: from a scoreboard to a teammate.
Strategic Segmentation: HR vs. Strategy Execution
A clear bifurcation has emerged in the vendor landscape, splitting tools into two distinct categories based on their operational focus:
- HR & People Success Focus: Platforms like Lattice and 15Five view OKRs through the lens of employee engagement, performance reviews, and career development. These tools are ideal for organizations where cultural alignment is the primary objective [9].
- Strategy Execution Focus: Platforms like WorkBoard, Quantive, and Profit.co view OKRs through the lens of business operations, enterprise portfolio management, and data integration. These are preferred by COOs and Strategy Officers in large enterprises where complex dependency mapping and automated reporting are critical [10].
Buyers must diagnose their primary friction point—is it employee disengagement (HR path) or strategic misalignment (Execution path)?—to select the appropriate solution category.
Business Implications of Failed Implementations
The cost of failed OKR software implementation extends beyond license fees. It creates "process fatigue," where employees become cynical about new management initiatives.
Key Failure Modes:
1.
Set and Forget: 60% of organizations fail to review OKRs outside of quarterly cycles, rendering the software a static repository rather than a management tool
[11].
2.
Over-Complexity: Implementing too many objectives (e.g., 10+ per team) dilutes focus. Successful implementations typically limit focus to 3-5 objectives to ensure clarity
[12].
3.
Lack of Data Maturity: Implementing advanced tracking software without basic data infrastructure leads to empty dashboards. If the underlying data (CRM, ERP, Project usage) isn't clean, the OKR software cannot automate progress
[11].
Future Outlook: 2026 and Beyond
As we look toward 2026, the standalone "OKR tool" market faces pressure to consolidate. The retirement of Viva Goals suggests that generalist productivity suites may struggle to maintain the depth required for serious strategy execution, pushing enterprises toward specialized vertical solutions.
We anticipate three major shifts:
1.
Consolidation of "Work" and "Goals": The separation between Project Management tools and OKR tools will blur. Expect major project management vendors to acquire or build deeper OKR capabilities to own the full "Strategy to Execution" stack.
2.
Standardization of Metrics: AI will drive the standardization of Key Results. Software will suggest industry-benchmark metrics (e.g., "SaaS Rule of 40") rather than relying on users to define success criteria from scratch.
3.
Algorithmic Management: AI will play a larger role in resource allocation, dynamically suggesting that teams swarm on lagging objectives based on real-time data flow.
For organizations navigating this complex ecosystem, success lies not in the software features, but in the operational rituals established around them. The software is merely the vessel for the strategy; without disciplined execution, even the most advanced AI-enabled platform will become digital shelfware.


